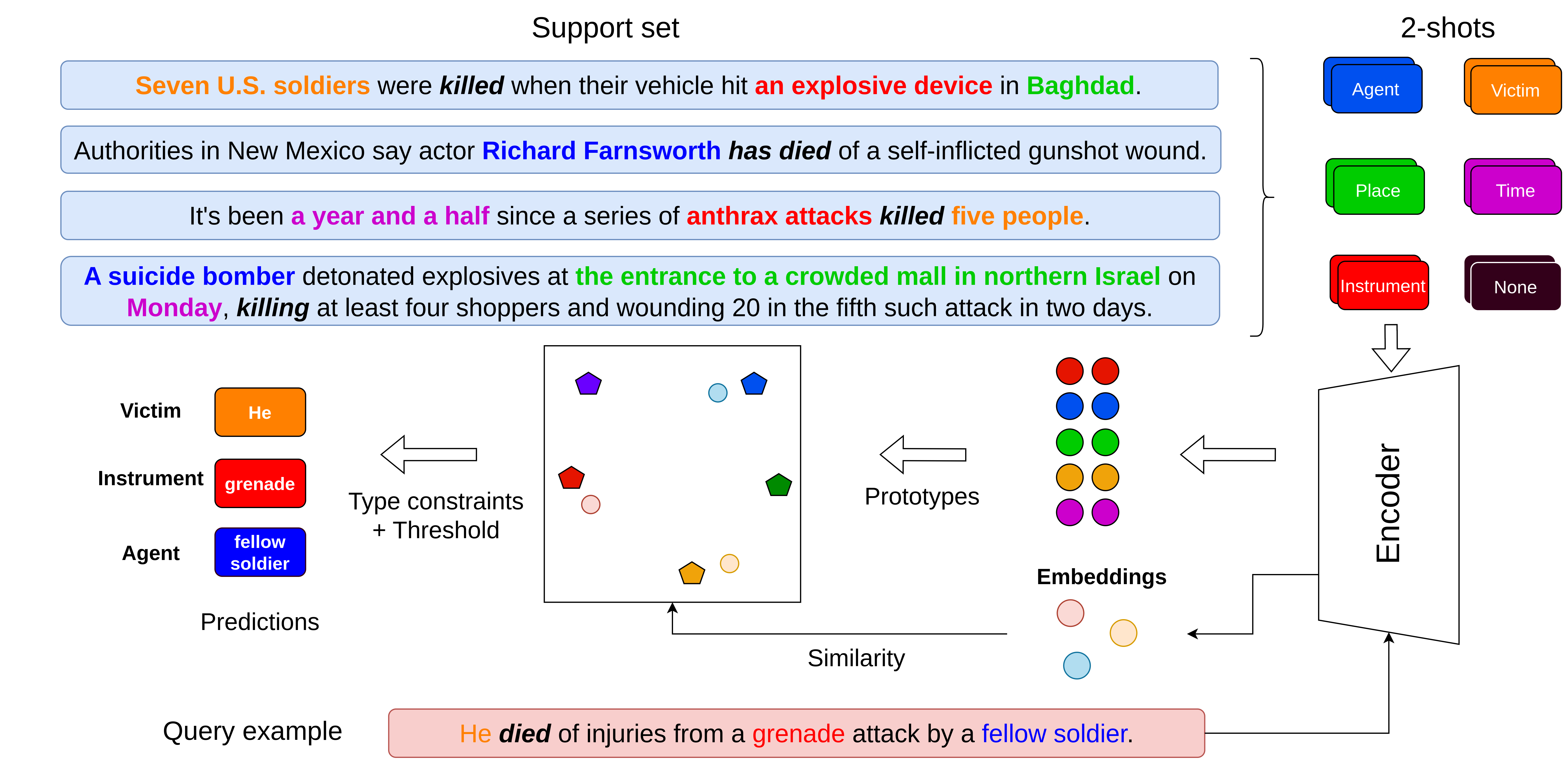
Few-Shot Event Argument Extraction Based on a Meta-Learning Approach
Few-Shot Event Argument Extraction: A Meta-Learning Approach
Introduction
In natural language processing, event argument extraction is a crucial task that involves identifying and classifying the arguments or roles associated with an event mentioned in a text. Our paper presents a meta-learning approach for few-shot event argument extraction, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets.
Methodology
Our approach combines two powerful techniques:
1. Prototypical Networks
- Creates prototype representations for each event argument role
- Utilizes distance-based classification in the embedding space
- Enables quick adaptation to new event types
2. Memory-Augmented Networks
- Maintains a dynamic memory of previous examples
- Facilitates better generalization across different event types
- Improves model adaptation with limited data
Implementation Details
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class ProtoNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
def forward(self, support_set, query_set):
# Encode support set
support_embeddings = self.encoder(support_set)
# Compute prototypes
prototypes = self.compute_prototypes(support_embeddings)
# Encode and classify query set
query_embeddings = self.encoder(query_set)
logits = self.compute_distances(query_embeddings, prototypes)
return logits
Experimental Results
Our method achieves significant improvements over baseline approaches:
| Model | F1 Score | Few-shot Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline BERT | 67.3 | 58.2 |
| ProtoNet | 72.1 | 63.5 |
| Our Method | 75.8 | 67.9 |
Key Findings
- Improved Generalization: Our meta-learning approach shows better generalization to unseen event types
- Efficient Learning: Requires significantly fewer examples to achieve competitive performance
- Robust Performance: Maintains consistent performance across different domains
Future Directions
We identify several promising directions for future research:
- Integration with pre-trained language models
- Extension to zero-shot scenarios
- Cross-lingual event extraction
- Dynamic prototype updating mechanisms
Conclusion
Our meta-learning approach effectively handles the challenge of limited annotated data, enabling robust and accurate extraction of event arguments from minimal examples. The combination of prototypical networks and memory augmentation provides a strong foundation for few-shot learning in event extraction tasks.
References
- Snell, J., Swersky, K., & Zemel, R. (2017). Prototypical networks for few-shot learning.
- Finn, C., Abbeel, P., & Levine, S. (2017). Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks.